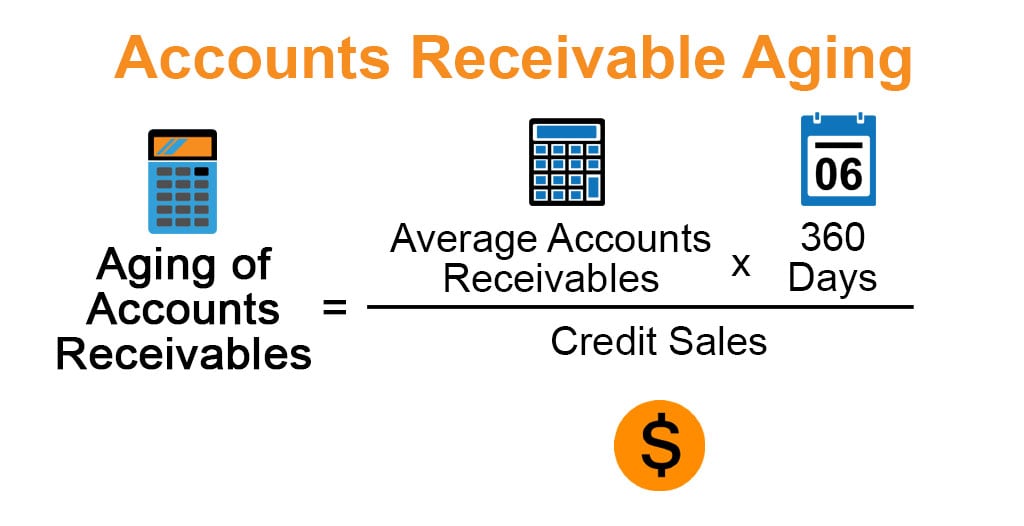
How Do You Calculate Aging Accounts Receivable?

The method used to estimate the desired balance in the allowance account is called the aging of accounts receivable. However, if you see multiple clients are late on payments, it why the irs discontinued the e might be an issue with your customer credit policy. If this is the case, you can compare your credit risk to industry standards to see if you’re taking too much credit risk.
Categorize Invoices
The accounts receivables aging method categorizes the receivables based on the range of time an invoice is due. The account receivables aging method sorts the unpaid invoices by date and number, and management uses the aging report to determine the company’s financial well-being. Without an accounts receivable aging report, it can be difficult to maintain a healthy cash flow and identify potentially bad credit risks to your business posed by doubtful accounts. To be useful, your report needs to include client information, the status of collection, the total amount outstanding, and the financial history of each client. An aging report lists a company’s outstanding customer invoices and payment due dates. Aging reports help track how long customers owe money to identify collection issues or determine credit terms.
Adjusting Credit Policies
An accounts receivable aging report groups a business’s unpaid customer invoices by how long they have been outstanding. An accounts receivable (AR) aging report organizes all your unpaid customer invoices based on how long they have been outstanding. The report is usually divided into intervals such as 0-15 days, days, days, and more than 45 days. Monitoring receivables with this report helps business owners identify why their business may be slowing down and which customers are becoming credit risks. An aging schedule is a tool used to categorize accounts receivable based on the length of time an invoice has been outstanding.
Accounts Receivable Aging: Definition, Calculation, and Benefits
Going back to the aging report, you can systematically assess how likely each invoice is to remain unpaid. Such calculations assist in adjusting your accounts and help understand the financial health of your business. Consistently high amounts in older categories might indicate a need to tighten credit policies or improve your collection strategies. For step two, use accounting software or spreadsheets to list the invoices. This list will include customer names, invoice numbers, dates, and outstanding amounts. These components provide a clear picture of your receivables along with supporting smooth collections and financial planning.
Calculating the Allowance for Doubtful Debts
Both the aging and percentage of net sales methods, as well as other methods, are used in practice. The total of these figures represents the desired balance in the account Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts. A credit entry is made to Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts, thereby adjusting the previous balance to the new, desired balance. The debit part of the entry is made to the Uncollectible Accounts Expense account. Amounts owed to a company by its customers for goods or services provided on credit. The longer past due an account goes the more doubtful it is that payment will be received.
- This is a business analysis ratio that will help you determine the average number of days it takes to collect your sales.
- Another tactic is to compare your accounts receivable performance against industry norms.
- This can make an aging A/R report misleading because if a customer pays just a few days later, it can show up as past due on the report.
How is the balance in the allowance account determined at year-end under the aging method?
The final step is to repeat the process from step 3 for all of your clients having unpaid invoices on their accounts. When this is done, you’ll be able to see each ‘bucket’ of overdue payments, giving you a much clearer sense of how much you’re owed for each client and how overdue your accounts are in general. If you do end up incurring a bad debt expense, you’ll need to provide evidence in the form of accounts receivable aging reporting (along with other documentation). While the percentage of net sales method is easier to apply, the aging method forces management to analyze the status of their accounts receivable and credit policies annually.
Accounts receivable aging sorts the list of open accounts in order of their payment status. There are separate buckets for accounts that are current, those that are past due less than 30 days, 60 days, and so on. Based on the percentage of accounts that are more than 180 days old, a company can estimate the expected amount of unpaid accounts receivables for future write-offs.
KPMM, LLC is a public accounting firm that bills clients after a tax return has been prepared. The clients are required to pay their invoice with 30 days of receiving it. KPMM has five different clients with a 100 balance owed—one in each category listed above. Once a method of estimating bad debts is chosen, it should be followed consistently.
The specific receivables are aggregated at the bottom of the table to display the total receivables of a company, based on the number of days the invoice is past due. For instance, if payment was due on January 15th, and it’s now January 25th, you would mark it as being 10 days past due. On the assumption that the longer an account is outstanding, the less likely its ultimate collection is, an increasing percentage is applied to each of these categories. The aging method involves determining the desired balance in the Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts. For example, if the invoice was due on the 15th and it’s now the 22nd, the invoice is seven days past due. As you apply these tactics, clearly outline the consequences of non-payment, such as legal action or halting the delivery of products and services.


